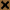The most extensively referenced industrial oil classification is the one established by ANSI/AGMA (American National Standard Institute/American Gear Manufacturers Association) that classifies industrial gear oils where gear oils are classified into four types as shown the following table:
- R&O gear oil is formulated to contain, as additives, rust inhibitor and oxidation inhibitor and is distributed as multi-purpose oil for various applications.
- EP gear oil contains extreme pressure agents such as S-P additive and it is used in large quantity than any other gear oil type. In addition.
- Compound type and (4) synthetic gear oil are used for special applications.
AGMA Gear Oil Classification for Enclosed Gear Units for Industrial Applications
| Gear Oil Type | Formulation | Operating Temperature Limit |
| R&O Type | Mineral oil containing oxidation inhibitor and rust inhibitor as additives | 200°F(93°C) |
| EP Type | Mineral oil containing extreme pressure agent as additive. Gear oil for enclosed gear unit uses naphthenic acid or S-P based extreme pressure agent. | 160(71°C) ~ 200°F |
| Compound Type | Mineral oil containing 3~10% of fatty oil or synthetic fatty acid (generally used for worm gears) | 160(71°C) ~ 200°F |
| Synthetic Type | Polyol Ester, Poly Glycol, and synthetic hydrocarbon based synthetic oil (used for enclosed gear units designed for special operating conditions or worm gears) |
AGMA Gear Oil Classification for Semi-Enclosed Gear Units and Open Gears for Industrial Application
| Gear Oil Type | Formulation |
| R&O Type | Mineral oil containing oxidation and rust inhibitor as additives |
| EP Type | Mineral oil containing naphthenic acid or S-P based extreme pressure agent as additive. |
| Compound Type | Straight mineral oil of high-viscosity grade or EP oil diluted with volatile non-flammable solvent (solvent-dilution type) |
In gear lubrication, the most important performance property is viscosity and, depending on the gear configuration, number of gear teeth, operating conditions, etc ., gear oil of appropriate viscosity needs to be selected. As for the viscosity classification of industrial gear oils. AGMA specifies it for high-viscosity grades, too. AGMA also adopted a viscosity number specifying kinematic viscosity from 37.8°C to 98.9°C as in open gear applications
ANSI/AGMA classification is used in general for viscosity classification of industrial gear oils. The following table shows the mapping between ISO viscosity classification and ANSI/AGMA viscosity classification:
|
Vis.mm2/s (40°C )
|
ISO VG |
AGMA | ||
| R&O | EP | Synthetic | ||
| 28.8 ~ 35.2 | 32 | 0 | – | 0S |
| 41.4 ~ 50.6 | 46 | 1 | – | 1S |
| 61.2 ~ 74.8 | 68.2 | 2 | 2EP | 2S |
| 90.0 ~ 110 | 100 | 3 | 3EP | 3S |
| 135 ~ 165 | 150 | 4 | 4EP | 4S |
| 198 ~ 242 | 220 | 5 | 5EP | 5S |
| 288 ~ 352 | 320 | 6 | 6EP | 6S |
| 414 ~ 506 | 460 | 7.7Comp | 7EP | 7S |
| 612 ~ 748 | 680 | 8.8Comp | 8EP | 8S |
| 900 ~ 1100 | 1000 | 8A.8AComp | 8AEP | – |
| 1350 ~ 1650 | 1500 | 9 | 9EP | 9S |
| 2880 ~ 3520 | – | 10 | 10EP | 10S |
| 4140 ~ 5060 | – | 11 | 11EP | 11S |
| 6120 ~ 7480 | – | 12 | 12EP | 12S |
| 190 ~ 220mm2/s @100°C | – | 13 | 13EP | 12S |